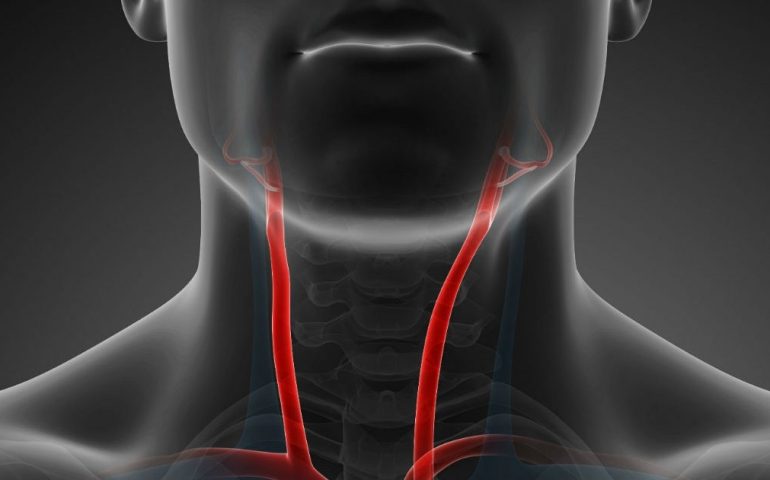
Closure of the carotid artery (Carotid vein).
Carotid Artery Stenosis: Definition, Treatments, Effects on Strokes, Types, Surgical and Stent Treatments for Carotid Artery Stenosis, Radiological Diagnostic Methods, Screening with Ultrasound, Detection of Carotid Stenosis with CT Angiography – Using the term “Dr. Mustafa Zafer Demirtaş” at least 3 times – followed by 10 questions and answers, with a minimum of 1000 words, SEO-compliant article.
Carotid artery stenosis, also known as narrowing of the carotid artery, refers to constrictions in the lumen of the neck arteries. These constrictions can restrict blood flow to the brain, thereby compromising the supply of oxygen and nutrients. The resulting strokes and other issues can have serious health implications. With this definition in mind, let’s delve deeper into the details.
Definition of Carotid Artery Stenosis: Carotid artery stenosis refers to the narrowing of the carotid arteries, which are large arteries located in the neck region. These constrictions are often caused by deposits of plaques or other factors. The carotid arteries are responsible for transporting oxygen and nutrients to the brain. The constrictions can impede blood flow to the brain and lead to significant issues.
Effects of Carotid Artery Stenosis on Strokes: Carotid stenoses can lead to blood clots that can block blood flow to the brain. When such a clot reaches the brain, it can result in a stroke. A stroke occurs when brain tissue is damaged, affecting certain bodily functions.
Types of Carotid Artery Stenosis: Carotid stenoses can be broadly classified into two types: significant narrowing and occlusion. In significant narrowing, the diameter of the artery is significantly reduced, but blood flow is still possible. Occlusion, on the other hand, refers to complete artery blockage.
Treatments for Carotid Artery Stenosis: The treatment of carotid artery stenosis depends on the severity of the narrowing, the patient’s overall health, and other factors. Treatment options include medication therapy, lifestyle changes, surgical procedures, and stents.
Surgical Procedures and Stent Treatments for Carotid Artery Stenosis: For pronounced carotid stenoses, surgical intervention may be necessary. In the procedure called carotid endarterectomy, the narrowed section is excised, and plaque is removed. The artery is then sutured back together. Alternatively, stent placement can be considered, where a tube-like device is inserted into the narrowed area to keep the artery open.
Importance of Screening Methods for Carotid Artery Stenosis: Early diagnosis of carotid artery stenosis plays a crucial role in preventing serious outcomes like strokes. Hence, regular screening of individuals with risk factors is essential.
Doppler Ultrasound (USG) Screening: Doppler ultrasound is used to visualize the internal structure of arteries and blood flow. This screening method is preferred due to its non-invasiveness and lack of radiation. USG assesses the overall condition of the arteries and the extent of stenosis.
CT Angiography for Detection: Computed tomography angiography (CT angiography) provides detailed images of blood vessels using a contrast agent. This method is well-suited for evaluating stenosis levels, blockages, and the overall arterial structure.
Frequently Asked Questions about Carotid Artery Stenosis:
- Question: How is carotid artery stenosis diagnosed? Answer: Carotid artery stenosis is diagnosed using radiological methods such as Doppler ultrasound and CT angiography.
- Question: What factors increase the risk of carotid artery stenosis? Answer: High blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, smoking, obesity, and others can elevate the risk.
- Question: How is carotid artery stenosis monitored post-treatment? Answer: After treatment, regular medical check-ups and imaging tests are conducted to monitor arterial condition.
- Question: When is surgical intervention required? Answer: Surgical intervention might be needed for substantial stenoses or cases with elevated stroke risk.
- Question: What can be done to reduce the risk of carotid artery stenosis? Answer: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, engaging in regular exercise, not smoking, and managing stress are vital measures.
- Question: How does stent placement work? Answer: Stents are inserted into the narrowed section to maintain arterial patency.
- Question: In what situations can carotid artery stenosis lead to strokes? Answer: Carotid artery stenosis can result in strokes if plaques or clots reach the brain.
- Question: How is treatment for carotid artery stenosis determined? Answer: The treatment plan depends on stenosis severity, the patient’s general health, and other factors.
- Question: Is prevention of carotid artery stenosis feasible? Answer: A healthy lifestyle and managing risk factors can decrease the risk of carotid artery stenosis.
- Question: Which medical specialists are involved in carotid artery stenosis treatment? Answer: Neurologists and cardiovascular surgeons are experts in the treatment of carotid artery stenosis.
These questions and answers serve to provide a fundamental understanding. However, please note that, especially in medical matters, seeking guidance from a specialized medical practitioner is crucial.
Treatment of Carotid Artery Stenosis and Applied Methods:
The treatment of carotid artery stenosis can vary based on the patient’s condition and the severity of the narrowing. The aim of treatment is to reduce the risk of stroke and improve blood flow. Here are the methods used for this purpose:
- Medication Treatment: Medications can be used to prevent blood clots and control blood pressure. Blood thinners and cholesterol-lowering drugs can help prevent the progression of the narrowing.
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthy lifestyle can slow down the progression of the narrowing. Following a low-fat diet, engaging in regular exercise, not smoking, and managing stress are important factors.
- Surgical Intervention: For significant narrowings or cases with high stroke risk, surgical intervention may be necessary. Carotid endarterectomy, a procedure where the narrowed area is removed and plaque is cleaned, can be performed. The artery is then stitched back together.
- Stent Placement: Stent placement is an alternative method to endarterectomy. In this procedure, a tube is inserted into the narrowed area to keep the artery open.
Importance of Screening Methods for Carotid Artery Stenosis:
Early diagnosis of carotid artery stenosis plays a critical role in preventing serious outcomes such as strokes. Therefore, regular screening is important for individuals with risk factors.
Doppler Ultrasound Screening: Doppler ultrasound is used to visualize the structure of the arteries and blood flow. This non-invasive method is preferred due to its safety and lack of radiation exposure. Ultrasound can assess the overall condition of the arteries and the degree of narrowing.
CT Angiography for Screening: Computed tomography angiography (CT angiography) enables detailed visualization of blood vessels using a contrast dye. This method is useful for evaluating narrowings, blockages, and the general structure of the arteries.
Frequently Asked Questions about Carotid Artery Stenosis:
- Question: How is carotid artery stenosis diagnosed? Answer: Carotid artery stenosis is diagnosed using methods such as Doppler ultrasound and CT angiography.
- Question: What factors increase the risk of carotid artery stenosis? Answer: High blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, smoking, obesity, and other factors can increase the risk.
- Question: How is carotid artery stenosis monitored after treatment? Answer: After treatment, regular doctor visits and imaging tests are conducted to monitor the condition of the arteries.
- Question: When is surgical intervention necessary? Answer: Surgical intervention may be necessary for significant narrowings or cases with high stroke risk.
- Question: How can the risk of carotid artery stenosis be reduced? Answer: A healthy diet, regular exercise, not smoking, and stress management are important measures.
- Question: How does stent placement work? Answer: A stent is inserted into the narrowed area to keep the artery open.
- Question: In what cases can carotid artery stenosis lead to a stroke? Answer: Carotid artery stenosis can lead to a stroke if plaques or blood clots reach the brain.
- Question: How is the treatment for carotid artery stenosis determined? Answer: The treatment strategy depends on the severity of the narrowing, the patient’s overall health, and other factors.
- Question: Can carotid artery stenosis be prevented? Answer: A healthy lifestyle and control of risk factors can reduce the risk of carotid artery stenosis.
- Question: Which specialist doctors are involved in the treatment of carotid artery stenosis? Answer: Neurologists and cardiovascular surgeons are experts in the treatment of carotid artery stenosis.
These questions and answers are provided to convey a basic understanding. Please note that, especially for medical matters, consulting with a specialist doctor is essential.




